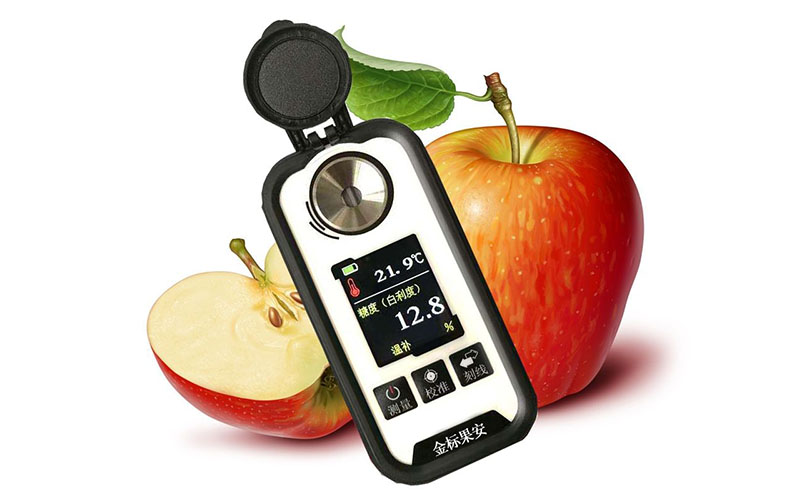
Foods have different amounts of sugar in them. The sugar content meter is the tool used to measure how much sugar something has. Hand-held sugar content meters, electronic desktop sugar content meters, and digital display sugar content meters are only a few of the several varieties of sugar content meters. They help find out the concentration or refractive index of solutions that contain sugar or do not contain sugar.
Why use a Fruit Brix Meter?
Sugar concentration determines fruit ripeness and quality. Traditional Brix value detection uses a hand-held Brix meter and fruit juice. In shops, sugar content marks the freshness and sweetness of fruit and vegetables. Customers can judge the quality of fruit and vegetables by their Brix value.
Properly evaluating fruit maturity helps fruit distributors and supermarkets determine when to store and sell fruit. Sample inspections are used to measure overall maturity. It is a simple method to measure the fruit’s Brix with a Brix meter to determine its maturity.
The portable fruit sugar content non-destructive testing device may not only reflect the fruit’s sugar content but also be used to create sweetness standards for different fruits, so that in fruit production and commerce, they just need to measure sugar. By comparing the fruit’s sugar level to its standard for sweetness, you can figure out how good it is and have a good basis for pricing and quality control.
Use this tool to measure the fruit’s sugar content on a large scale before picking. Ensure uniform sugar content and fruit quality to increase revenues.
Use this product to test the amount of sugar in fruit while packing it to get the best results when grading, sorting, processing, and packaging fruit.
It doesn’t damage the fruit, keeps it intact, and promptly detects batches; it’s used for cultivation guiding, maturity monitoring, quality evaluation, etc.
The portable fruit sugar content non-destructive tester uses near-infrared spectroscopy and chemometric analysis, etc.
What is the difference between a digital glucometer and a handheld refractometer?
Digital Brix Meter:
The Digital Brix Meter measures weight percent concentration or refractive index in sugar-containing liquids, widely utilized in the sugar, food, beverage, agricultural, and scientific industries.
How it works: The glucometer employs the refraction phenomenon when light enters another medium from one medium, and the refractive index is constant. Using the soluble substances in the sugar solution and the refractive index, the sugar meter/refractometer can calculate the sugar concentration.
• Handheld Refractometer
Hand-held refractometers, also called sugar mirrors, measure the soluble solid content (sugar content) of fruits and vegetables to determine their quality and maturity. Sugar meters are cylinder-shaped. Put the sugar liquid to be measured in the back groove, wipe it evenly, close the lid, and then point the sugar meter to the light.
The handheld refractometer measures nD and nF-nC of transparent, translucent liquids or solids (which is mainly used to measure transparent liquids). If the device has a thermostat, the refractive index ND can be monitored from 070. Refractive index and average dispersion are significant optical constants used to understand optical characteristics, purity, concentration, and dispersion size. Hand-held refractometers are used in the petroleum, oil, paint, food, everyday chemicals, and sugar industries to quantify sugar concentration in sucrose solutions. It’s essential for companies, schools, and geological and industrial research.
What are the factors that affect the test results of the glucometer?
Fruit growers need to pay close attention to how ripe and sweet their fruit is. Using a hand-held sugar meter, we can tell how ripe the fruit is by how much sugar it has. But the results of a test done with a hand-held glucometer can be affected by things like:
Peel color: In the early and middle stages of melon growth, the peel is usually green. However, on the side that touches the ground, the epidermis has trouble breathing because of the moist soil and long exposure to dark light. This causes the chlorophyll in the fruit epidermis to break down, making the skin white or yellow. As the fruit ripens or is exposed to sunlight, the rind of some fruits turns yellow or white. There is a big difference between how things are measured in the dark and in the light.
Light intensity: Analysis shows that ambient light also has a big effect on the test results of the handheld sugar meter, and that the two are related in a positive way. However, when the light intensity doesn’t change much, it doesn’t have a big effect on the test results.
Using a hand-held sugar meter to find out how good the fruit is on the inside is very important for agriculture, scientific research, and fruit development. Under the assumption that it won’t change the quality of the fruit, finding out what nutrients are inside the fruit has become a new market need.
How to use a hand-held refractometer to measure sugar?
By using a handheld refractometer to measure the amount of total soluble solids (TSS) in fruits and vegetables, you can get a rough idea of how much sugar they have.
When light goes from one medium to another and the ratio of the sine of the incident angle stays the same, this is called refraction. The refractive index is the name for this number. Under certain conditions, the amount of soluble solids in fruit and vegetable juice is equal to the refractive index (the same temperature and pressure).
A refractometer, also called a refractometer, is an instrument that measures how concentrated a liquid is by using light. It is used to measure the refractive index, birefringence, and other optical properties. The index of refraction is one of the most important constants of matter. Many pure things have a certain index of refraction. If there are impurities in the substance, the index of refraction will change, and there will be deviations. The deviation will be bigger if there are more impurities.
1) Putting the instrument in place: Set the refractometer on a table near a window or in front of a light bulb. But don’t put the instrument in direct sunlight to keep liquid samples from evaporating quickly. Connect the water intake of the measuring prism’s thermal insulation jacket to the super constant temperature tank with a rubber tube. The constant temperature is based on the refractometer’s thermometer.
2) Add sample: Loosen the lock button, open the auxiliary prism, put its frosted slope in a horizontal position, and use a burette to add a small amount of acetone to clean the mirror surface so that the non-volatile dirt can escape. If you need to, gently dry the surface of the mirror with lens tissue, but don’t use filter paper.
After the mirror surface is dry, put a few drops of sample on the rough mirror surface of the auxiliary prism, close the auxiliary prism, and tighten the lock knob. If the sample is volatile, it can be added from the liquid addition tank when the two prisms are almost closed. Then, close the two prisms and lock the lock button.
3) To turn on: Turn the handle until the number on the dial scale is at its lowest point. Then, adjust the reflector so that light from the outside enters the prism group. Finally, look through the measuring telescope to make the field of view as bright as possible. Set the eyepiece so that the view is as clear as possible.
4) Coarse adjustment: Turn the handle to slowly raise the value on the dial scale until a colored light band or a black-and-white critical line appears in the field of view.
5) Without color: Turn the achromatic handle to make a clear line of light and dark appear in the field of view.
6) Fine adjustment: Turn the handle until the critical line is right where the X-shaped “wires” meet. If it is still a little bit spread out, the anti-dispersion handle needs to be changed so that the critical line can be seen.
7) Reading: The reading is there to keep the dial from getting dirty. The dial is usually put in the cover of the refractometer. To read, first open the small window above the cover to let light in. Then, use the reading telescope to look at the corresponding number on the scale.
To reduce unintended errors while assessing whether the critical line is at the quasi-wire point, spin the handle and measure three times. How the sample is made affects the refractive index in a very sensitive way. Slight changes in the sample’s composition can cause false readings due to contamination or evaporation of volatile components. Because of this, a sample needs to be measured. Repeat the sampling three times, measure the data from these three samples, and take the average value.
FAQ:
What is the unit of fruit sugar content?
Sugar content is the soluble solids in liquid food. Generally, sugar content is measured by sugar meter/glucometer, and its unit is Brix (degree).
What does BRIX (%) mean?
Brix is a scale that is based on how much sucrose is in 100 grams of sucrose that has been dissolved in water. ICUMSA data is used to find the conversion value between Brix and refractive index. If granulated sugar is the main soluble solid in the sample, the BRIX value can be called Brix. When measuring a sample with soluble solids other than sugar, like a seasoning, the BRIX value can be thought of as the sample’s total concentration of soluble solids. If you measure pharmaceutical and chemical samples, you need to make a conversion table from BRIX to sample concentration.